Focusing on cell adhesion molecules of the integrin family and their signaling pathways, the group “Molecular and Cellular Radiobiology” has made considerable contributions to the molecular understanding of cell adhesion-mediated radioresistance (CAM-RR) and cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR).
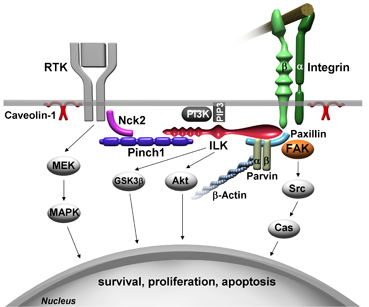
Signaling cascades of integrins and their interactions with transmembrane growth factor receptors are involved in the regulation of cell fate upon treatment with anticancer agents. The scheme on the right delineates a selection of molecules investigated by this research group.
Integrins, their interactions with transmembrane growth factor receptors (receptor-tyrosine-kinase, RTK) and intracellular signaling and adapter proteins. The scheme delineates a selection of molecules investigated by the research group members of “Molecular and Cellular Radiobiology” (published in Cordes N, Hehlgans S, Eke I. Adhesion, Invasion, Integrins and Beyond. In Medical Radiology - Radiation Oncology. Vol.: The Impact of Tumor Biology on Cancer Treatment and Multidisciplinary Strategies. Eds.: M. Molls, A.J. Giaccia, C. Nieder, M.S. Anscher. Springer-Verlag Heidelberg, 2009).
Main aims of this research group are:
- Understanding the molecular and cellular response of cells to ionizing radiation
- Identification of tumor-specific target molecules critically involved in tumor cell radio- and chemoresistance
- Untangling of the molecular and cell biological mechanisms of how a specific target molecule mediates radio- and/or chemoresistance in tumor cells
- Designing targeting strategies to inhibit these radio/chemosensitivity-related target molecules and translating these approaches from bench to bedside
To achieve the above mentioned goals, a variety of methodologies are performed by this group with a particular focus on more physiological 3D cell culture models:
- Colony formation assay
- Cell proliferation
- SDS-PAGE and Western blotting
- siRNA and gene transfection
- Signal transduction
- 3D growth
- Spheroids
- Histology (immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence)
- Apoptosis
- Immunoprecipitation and mass spectrometry (in cooperation)
- Proteome- and phosphoproteome analysis (in cooperation)
- DNA microarray analysis (in cooperation)
- Cell migration and invasion.







